ASTM A53
- Home
- /
- ASTM A53
World-Class Manufacturing
Advanced ERW technology ensures precision, strength, and international quality standard compliance.
Comprehensive Product Range
Extensive pipe sizes meet diverse plumbing, construction, and industrial application needs.
Uncompromising Quality Standards
Rigorous testing guarantees every pipe exceeds international quality and safety expectations.
Our Mission
Delivering world-class pipes strengthening infrastructure through innovation and quality manufacturing excellence.
Our Vision
Leading Middle East steel manufacturing with excellence, reliability, and innovative solutions.
Our Goals
Producing international-standard pipes through advanced technology and skilled workforce development programs.
OUR SPECIALTY
The Backbone of Modern Construction
Our round pipes are used in buildings, water systems, and industrial projects all over Saudi Arabia. They're strong, durable, and made to last for decades.


STRUCTURAL STRENGTH
Perfect for Frames and Structures
Square tubes are ideal for building frameworks, gates, fences, and structural supports. We make them in all the sizes you need.
VERSATILE SOLUTIONS
Multi-Purpose Pipes for Any Job
From industrial shelving to construction frameworks, our rectangular tubes work for all kinds of projects. Quality guaranteed.

ASTM A53: Your Complete Guide to Steel Pipe Standards and Specifications
What is ASTM A53?
If you work with steel pipes, you’ve probably heard about ASTM A53. It’s one of the most widely used pipe standards in the world. This specification covers both seamless and welded steel pipes, and it’s your go-to standard for mechanical and pressure applications.
Here’s what makes it special. ASTM A53 covers both black pipes and hot-dipped galvanized pipes. Whether you’re building a water system or installing industrial piping, this standard has you covered. It sets clear rules for quality, so you know exactly what you’re getting.
Think of ASTM A53 as the industry’s quality benchmark. When you specify these pipes, you’re choosing proven reliability. Manufacturers worldwide follow this standard to ensure their products meet strict requirements.
Understanding the Three Types of ASTM A53 Pipes
Not all ASTM A53 pipes are created equal. The standard breaks them down into three distinct types, and each one serves a different purpose.
Type F pipes use an old-school method called furnace butt welding. They’re perfect for everyday applications where you need reliable performance without breaking the bank. Many contractors love them for standard plumbing and construction jobs.
Type E pipes step things up with electric resistance welding. The welding process creates stronger bonds between the pipe edges. If your project involves higher pressures, these pipes are worth the extra investment.
Type S pipes are the premium option. They’re seamless, which means there’s no weld line at all. Industries that can’t afford any weak spots choose Type S. Yes, they cost more, but the peace of mind is priceless.
What’s Inside These Pipes? The Chemistry Matters
You might wonder why chemical composition matters for a pipe. Well, it makes all the difference in performance. ASTM A53 doesn’t leave this to chance.
Carbon content stays within strict limits. Too much carbon makes pipes brittle. Too little means they won’t be strong enough. The standard hits the sweet spot.
Manganese helps with strength and hardness. The specification requires just the right amount. Engineers have spent decades perfecting these ratios.
Now, phosphorus and sulfur are troublemakers. They can weaken your pipes over time. That’s why ASTM A53 keeps them to bare minimums. Every batch gets tested to make sure.
Silicon content varies depending on which type of pipe you’re buying. The standard spells out exactly what’s acceptable. No guesswork involved.
Strength That You Can Count On
Let’s talk about what really matters: how strong are these pipes? ASTM A53 gives you two grades to choose from, and the difference is significant.
Grade A pipes must handle at least 48,000 psi of tensile strength. That’s plenty strong for most applications. The yield strength sits at 30,000 psi minimum. For standard construction work, Grade A does the job beautifully.
Grade B pipes are the heavy hitters. They offer 60,000 psi tensile strength and 35,000 psi yield strength. When engineers need extra muscle, they specify Grade B. The cost difference is usually worth it for demanding applications.
Both grades must pass elongation tests. This measures how much the pipe can stretch before breaking. Nobody wants brittle pipes that crack under pressure. The elongation requirement ensures your pipes have some give when they need it.
Where You’ll Find These Pipes in Action
Walk around any city, and you’re surrounded by ASTM A53 pipes. They’re everywhere, quietly doing their job.
Municipal water systems depend on them heavily. Your tap water probably flows through ASTM A53 pipes at some point. Cities trust them because they last for decades with proper installation.
Construction sites are full of these pipes. They form building frames, scaffolding, and structural supports. Contractors know they can rely on their load-bearing capacity. Safety regulations often require them for good reason.
Industrial plants use ASTM A53 pipes for everything from steam lines to chemical processing. High temperatures don’t faze them when you choose the right grade. Chemical plants need that kind of reliability.
Your office building’s HVAC system? Probably uses ASTM A53 pipes. They handle temperature swings without losing integrity. Comfort depends on pipes that work year after year.
Fire sprinkler systems are another big application. When lives are on the line, you need pipes you can trust. Safety codes frequently specify ASTM A53 for exactly this reason.
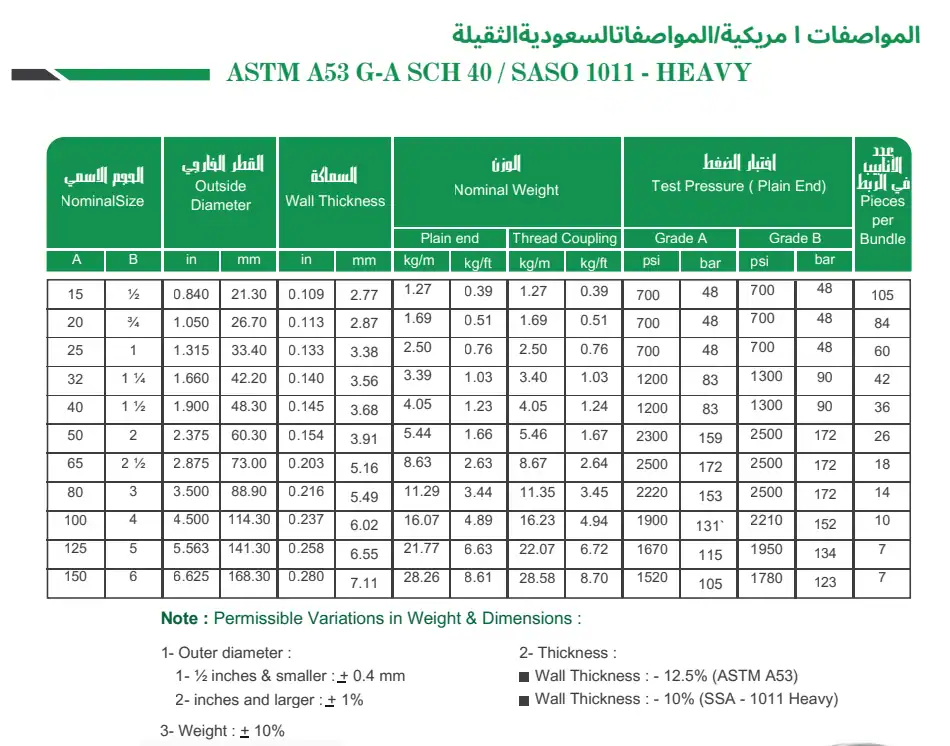
Sizes for Every Project
ASTM A53 pipes come in a huge range of sizes. The smallest standard size is half an inch. The largest reaches 26 inches in diameter. Need something bigger? Manufacturers can produce custom sizes.
Wall thickness matters just as much as diameter. Schedule 40 is the most common for everyday use. Schedule 80 handles higher pressures. Schedule 160 is for extreme applications. Your engineer will specify the right schedule based on your needs.
Standard lengths are typically 20 or 40 feet. But here’s the thing: you’re not locked into those lengths. Custom cutting is available when your project demands it.
Testing Ensures Quality Every Time
Before any ASTM A53 pipe leaves the factory, it goes through serious testing. These aren’t just quick checks. We’re talking about thorough quality assurance.
Hydrostatic pressure tests push pipes to their limits. Each one must hold the specified pressure without leaking or bursting. This test proves the pipe can handle real-world conditions.
Flattening tests check the welds on welded pipes. Technicians flatten the pipe to see if the weld holds. Any cracks mean rejection. It’s a tough test, but it catches weak welds.
Flaring tests examine the pipe ends. They flare the opening to a specific angle. The pipe must do this without cracking. This ensures you can work with the pipe during installation.
Chemical analysis happens in the lab. Technicians verify that the steel composition matches the specification. Every element gets measured. Documentation proves the pipe meets standards.
Choosing Between Black and Galvanized
You have two coating options with ASTM A53 pipes, and the choice matters.
Black pipes come without any coating. They’re pure steel, which keeps costs down. For indoor applications where moisture isn’t an issue, black pipes work perfectly well. Many heating systems use black pipes successfully.
Hot-dipped galvanized pipes get a zinc coating bath. This adds a protective layer that fights rust and corrosion. Outdoor applications need this protection. Water lines benefit hugely from galvanization.
The zinc coating thickness follows specific requirements. Thicker coatings last longer but cost more. If your pipes face harsh conditions, spend the extra money. Coastal areas with salt air definitely need the thicker coating.
How ASTM A53 Compares to Other Standards
People often ask how ASTM A53 stacks up against other specifications. Let’s clear that up.
ASTM A106 is similar but only covers seamless pipes. It’s designed for higher temperature applications. When temperatures really climb, A106 becomes the better choice. For general use, ASTM A53 offers more flexibility.
API 5L serves the oil and gas pipeline industry. It has even stricter requirements because of the critical applications. ASTM A53 handles general industrial needs perfectly.
International standards like ISO 65 align closely with ASTM A53. This global compatibility makes procurement easier. You can source pipes from different countries with confidence.
How These Pipes Are Made
The manufacturing process is fascinating. Let’s start with seamless pipes.
Manufacturers begin with solid steel billets. These get heated red-hot, then pierced to create the hollow center. Rolling mills stretch and shape the pipe to final dimensions. No welding needed. That’s why seamless pipes command premium prices.
Welded pipes start differently. Flat steel strips get formed into a tube shape. The edges meet and get welded together using electric resistance or furnace methods. Modern welding creates incredibly strong joints.
Heat treatment comes next for most pipes. This process relieves internal stresses that build up during manufacturing. The result is better mechanical properties and longer service life.
Quality control never stops during production. Workers check dimensions constantly. Surface inspection catches defects before pipes ship. This attention to detail is why ASTM A53 pipes perform so well.
Installing ASTM A53 Pipes Correctly
Proper installation makes all the difference. Even the best pipes fail if installed incorrectly.
Start by cutting pipes with the right tools. Band saws or pipe cutters work best. Always smooth the cut edges completely. Rough edges cause problems down the line.
Threading requires attention to detail. Follow the standard thread specifications exactly. Clean threads prevent leaks and allow proper sealant application. Don’t rush this step.
Support spacing depends on pipe size and orientation. Your engineering specifications will spell this out. Too much space between supports causes sagging. That puts stress on joints and can lead to failures.
Joining methods matter too. If you’re welding, make sure the welder is qualified. Threaded connections need proper torque. Too tight damages threads. Too loose causes leaks. Follow manufacturer guidelines.
Keeping Your Pipes in Good Shape
Regular maintenance extends pipe life significantly. A little attention goes a long way.
Inspect pipes periodically for corrosion signs. Catch rust early and you can treat it. Wait too long and you’re replacing sections. Visual inspections cost almost nothing.
Monitor pressure levels in your system. Sudden pressure drops tell you something’s wrong. Investigate immediately. Small problems become big ones fast.
Clean pipes when scale builds up. Hard water deposits reduce flow capacity. Use approved cleaning methods that won’t damage the pipe interior.
Never try to repair seriously damaged sections. Replace them instead. Your safety and system reliability depend on this. Temporary fixes rarely work long-term.
What You’ll Pay for Quality
ASTM A53 pipes offer excellent value for money. Let’s break down the costs.
Grade A pipes cost less than Grade B. The difference reflects the higher strength requirements. For many applications, Grade A provides all the strength you need.
Seamless pipes cost more than welded ones. The manufacturing process is more complex. If your application allows welded pipes, you’ll save money without sacrificing much.
Galvanized pipes run higher than black pipes. That zinc coating adds processing steps. But for outdoor use, it’s money well spent. Replacing rusted pipes costs far more.
Buying in bulk brings prices down. Plan your procurement to maximize savings. Consider your entire project needs upfront.
Quality certification might add a small premium. But documented compliance protects you. If someone questions your pipe specs, you have proof.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting pipe specifications seems complicated, but it doesn’t have to be.
Start by considering your operating conditions. What temperatures will the pipes face? What pressures? Corrosive chemicals in the mix? These factors narrow your choices quickly.
Evaluate the mechanical properties you need. High-stress applications demand Grade B. Standard uses work fine with Grade A. Don’t overspend on strength you don’t need.
Check applicable codes and regulations. Building codes often specify minimum requirements. Some industries have their own standards. Compliance isn’t optional.
When in doubt, consult with qualified engineers. Their expertise prevents expensive mistakes. A few hours of consultation beats costly do-overs.
Why ASTM A53 Remains the Top Choice
After decades in the industry, ASTM A53 pipes continue dominating the market. There are good reasons for this.
Reliability is proven through countless successful installations. These pipes work in every climate and application imaginable. That track record speaks volumes.
Consistent quality eliminates surprises. Every ASTM A53 pipe meets the same strict standards. You know what performance to expect. Project planning becomes much easier.
Availability is rarely an issue. Suppliers stock common sizes and can get special orders quickly. This keeps your project on schedule. Delays cost money.
Pricing stays competitive without compromising quality. You get solid performance at reasonable costs. Budget constraints don’t force you to sacrifice safety.
Technical support is readily available. Manufacturers provide guidance on proper selection and use. Success depends on choosing and installing the right pipe. Help is there when you need it.